Understanding Small Fiber Neuropathy
Before diving into exercise strategies, it’s essential to grasp the nature of SFN. Unlike other forms of neuropathy that affect larger nerve fibers, SFN predominantly targets the small nerves responsible for transmitting sensory information.
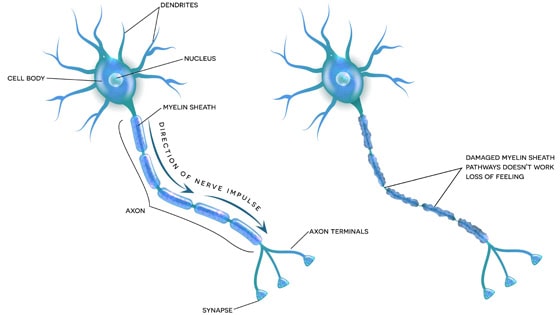
A healthy nerve functions like a well-tuned orchestra, with signals conducting smoothly and efficiently, whereas a damaged nerve resembles a disrupted symphony, with scattered notes and misfires causing sensory disturbances and pain.
This disruption can result in various symptoms, including burning pain, tingling sensations, and heightened sensitivity to touch or temperature changes.
What Causes Small Fiber Neuropathy
Small fiber neuropathy (SFN) can be caused by various factors, including:
- Autoimmune disorders like Sjögren’s syndrome and lupus.
- Metabolic conditions such as diabetes.
- Infectious diseases like HIV and Lyme disease.
- Exposure to toxins.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Idiopathic, meaning the cause is unknown.
In each case, the damage typically affects the small nerve fibers responsible for transmitting sensory information, leading to symptoms such as pain, tingling, and numbness in the affected areas.
Exercise and Small Fiber Neuropathy
While exercise might seem counterintuitive for those experiencing pain and discomfort, tailored physical activity can offer profound benefits for SFN management.
Engaging in regular exercise helps improve blood circulation, enhances nerve function, and promotes the release of endorphins, natural pain-relieving hormones. Moreover, maintaining a healthy weight through exercise can alleviate pressure on nerves, potentially reducing symptoms associated with SFN.
Designing an Exercise Program
Crafting an exercise regimen tailored to individuals with SFN requires a comprehensive understanding of their condition, limitations, and goals.
This is where a health and wellness consultant plays a pivotal role. By collaborating with a consultant, individuals can receive personalized guidance and support to develop an exercise plan that is safe, effective, and enjoyable.



